| Fields of Application: Automotive, Power, Lighting, Medical, Consumer, Telecom/Data, New Energy |
| Product Type |
Application Function |
Circuit Application |
Waveform |
Requirements |
Special Characteristics |
|
MKS 2
MKS 4
MKP 2
MKP 4 (HF-coupling/
decoupling) |
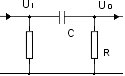
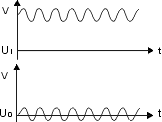
Blocking/Coupling
High-pass filter:
| – |
preventing DC voltages |
| – |
transferring AC voltages |
|
 |
 |
| – |
High insulation resistance |
| – |
Low self-inductance (to observe voltage rating) |
|
Metallized film capacitors (MK-types):
- High capacitance values in small box sizes
- ΔC/C over temperature: very low
- Self-healing capability-> high withstanding voltage, high reliability
- Very low dissipation factor (MKP)
- High-frequency application (MKP) due to low dissipation factor
|
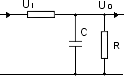
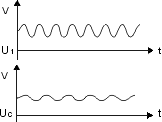
| Bypass/Decoupling
Low-pass filter:
| – |
suppressing transmission of high frequencies (AC voltages) |
|
 |
 |
| – |
High insulation resistance |
| – |
Low self-inductance |
|
|
MKS 2
MKS 4
MKP 4 |
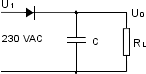
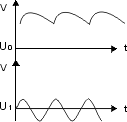
Smoothing
| – |
smoothing of pulsating DC-voltages from AC-rectifier |
|
 |
 |
| – |
Comparably high capacitance |
| – |
Low dissipation factor (to observe frequency) |
|
MKP 2
MKP 4
|
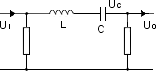
Band-pass filter (e.g. audio, TV)
| – |
pass frequencies within a certain range |
| – |
attenuate frequencies outside that range |
|
 |
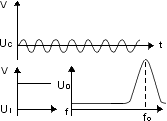 |
| – |
Low dissipation factor |
| – |
Stable capacitance |
|
Band-stop filter (e.g. audio, TV)
| – |
attenuate frequencies within a specific range |
| – |
pass frequencies outside that range |
|
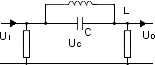 |
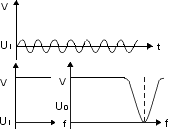 |
| – |
Low dissipation factor |
| – |
Stable capacitance |
|
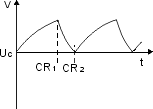
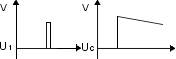
Timing (e.g. signal light)
| – |
when capacitor is charged voltage is increasing over time |
| – |
after passing certain value a new state change occurs |
|
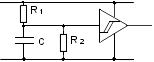 |
 |
| – |
High insulation resistance |
| – |
Stable capacitance |
|
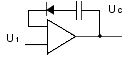
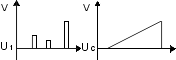
Sample & hold (e.g. amplifier) analogue-digital converter:
| – |
capacitor is used to store analogue voltage value |
| – |
electronic switch is used to connect/disconnect capacitor from analogue input (sampling rate) |
|
 |
 |
| – |
Low dielectric absorption |
| – |
High insulation resistance |
|
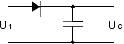
Peak voltage detectors
| – |
diode conducts positive „half cycles“ to charge capacitor to peak voltage |
| – |
DC "peak" stored in the capacitor, the diode is blocking current flow |
| – |
capacitor retaines the peak value even if the waveform drops to zero |
|
 |
 |
| – |
Low dielectric absorption |
| – |
High insulation resistance |
|